US Foreign Policy
The Policymaking Process
Michael E. Flynn
Kansas State University
Updated: 2024-09-23
Lecture Overview
Policymaking versus decision-making
Organization of policymaking
Influence of policy on decisions
Pitfalls in policymaking and decision-making processes
Key Questions
What is the difference beteween policymaking and decision-making?
What are the origins of policymakers preferences?
What are some of the key institutions and/or roles in the policymaking process?
Policy v Decision
Policy v Decision
Policy: Plans for broad classes of future contingencies
vs.
Decision: Choices for dealing with immediate problems
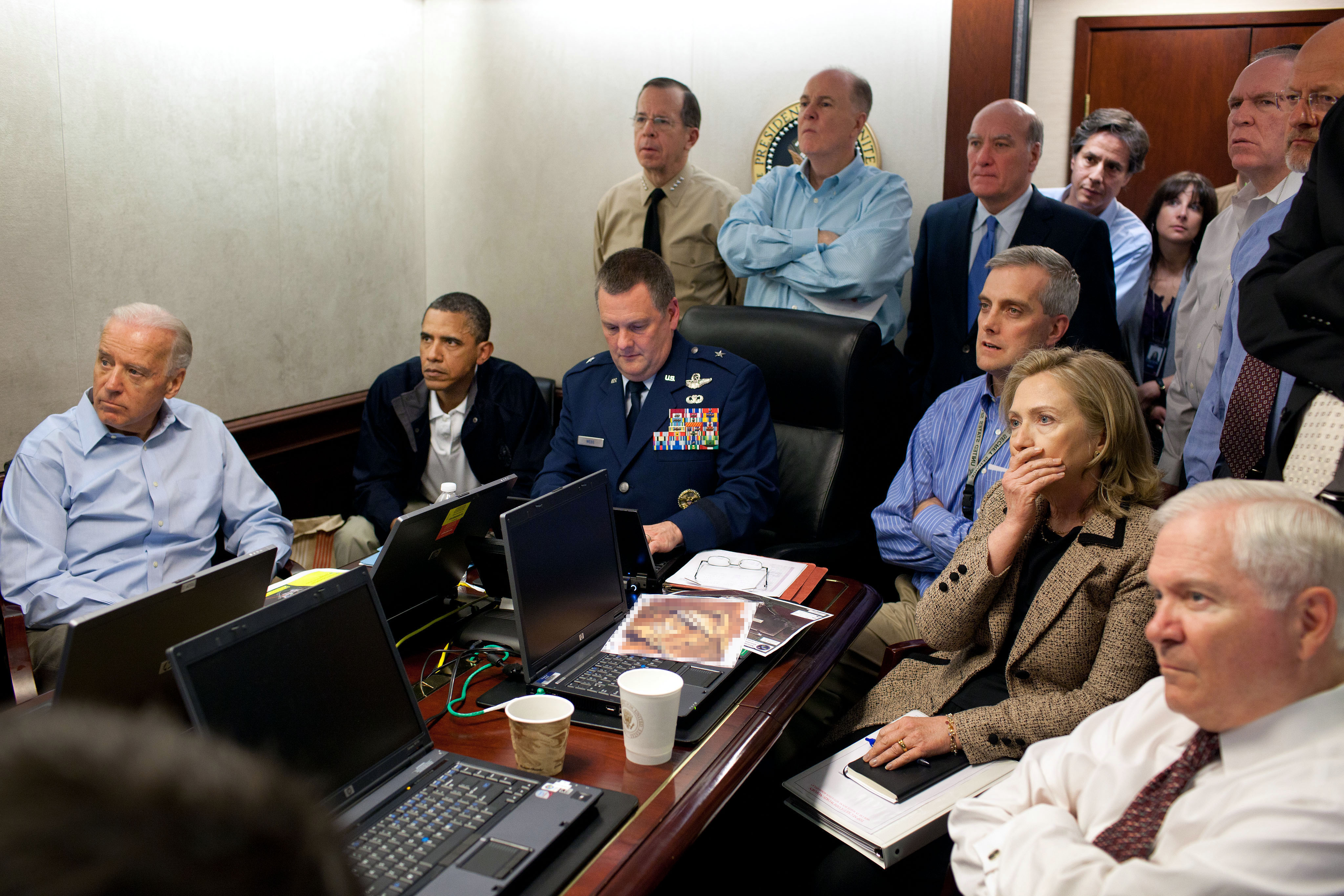

Situation room photo from bin Laden raid.
- Example of decision-making.
- US officials had to decide whether or not they wanted to capture bin Laden alive or to kill him. They also had to decide whether or not to release photos of bin Laden’s body. Secretary of Defense Robert Gates recently came out and said that one of the major factors leading them to decide not to release the photos as the possibility that they could be photoshopped, which they believed would inflame tensions and possibly endanger US military forces on the ground.
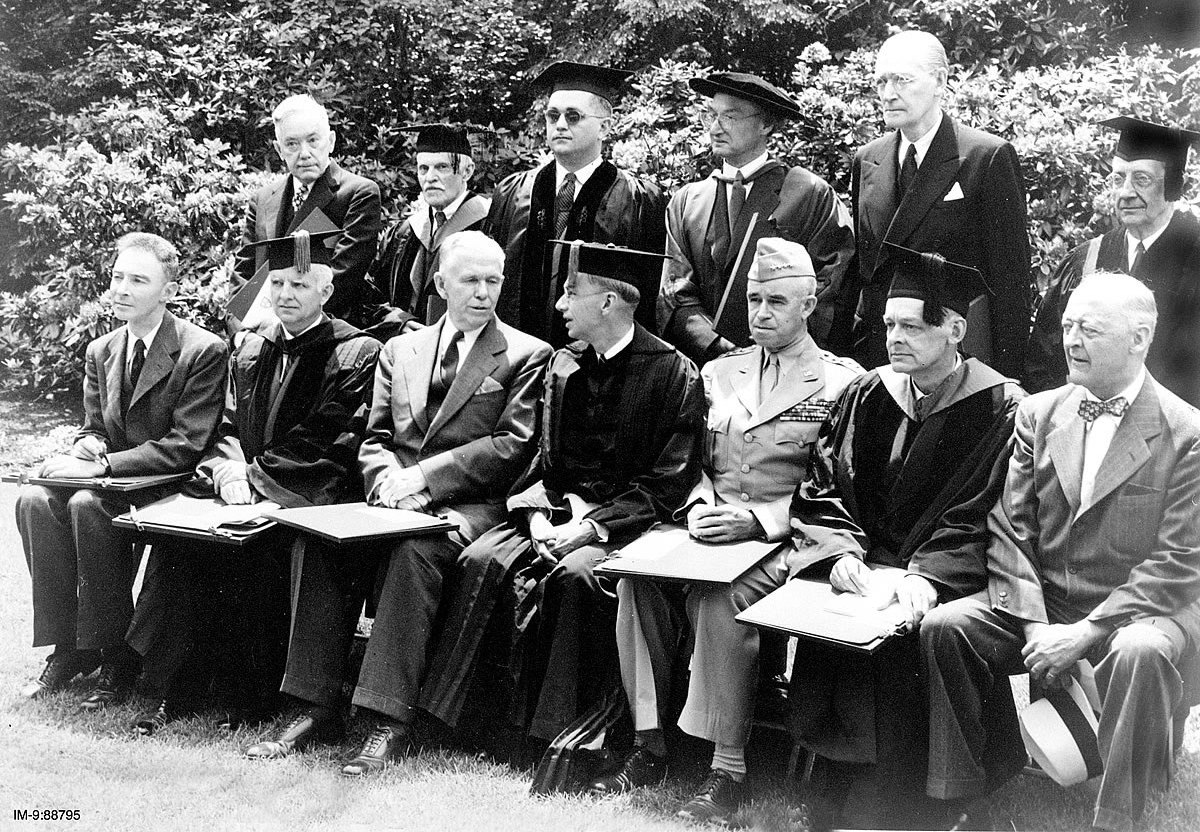

George Marshall at Harvard’s commencement address in 1947.
- Example of Policy.
- This set the stage for the Marshall Plan and for US policy more broadly.
- Excerpt from Marshall’s speech: Aside from the demoralizing effect on the world at large and the possibilities of disturbances arising as a result of the desperation of the people concerned, the consequences to the economy of the United States should be apparent to all. It is logical that the United States should do whatever it is able to do to assist in the return of normal economic health in the world, without which there can be no political stability and no assured peace. Our policy is directed not against any country or doctrine but against hunger, poverty, desperation and chaos. Its purpose should be the revival of a working economy in the world so as to permit the emergence of political and social conditions in which free institutions can exist. Such assistance, I am convinced, must not be on a piece-meal basis as various crises develop. Any assistance that this Government may render in the future should provide a cure rather than a mere palliative. Any government that is willing to assist in the task of recovery will find full cooperation, I am sure, on the part of the United States Government. Any government which maneuvers to block the recovery of other countries cannot expect help from us. Furthermore, governments, political parties or groups which seek to perpetuate human misery in order to profit therefrom politically or otherwise will encounter the opposition of the United States. Soviets initially invited to partake, but they decided to leave the Paris negotiations.
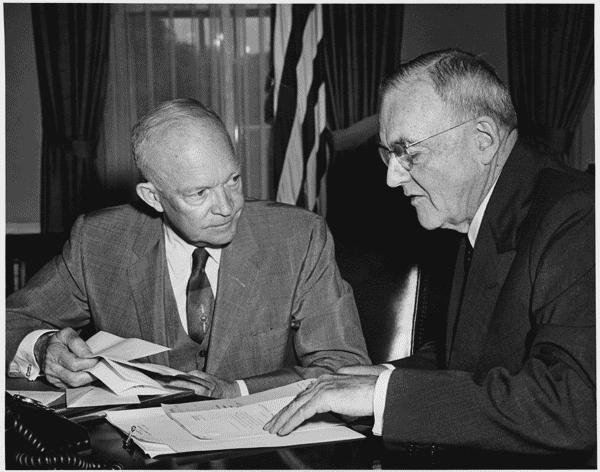

Eisenhower’s “New Look” Policy
- Eisenhower came into office concerned about maintaining the health of the economy while also meeting the demands of the Cold War. Nuclear weapons offered a relatively inexpensive way to deter aggression, but relied on the idea of massive retaliation.
- Problems with this policy were somewhat obvious:
- Salami tactics: Would the US seriously respond to small wars and incursions with full nuclear force?
- Nuclear weapons could potentially destroy the very thing we were trying to protect.
- Eisenhower also relied on covert missions, but these could be too small to effect real change or respond to a conventional military threat if needed. Massive retaliation thus left the middle ground between small fights and full nuclear war mostly open.
- Different processes at work
Policymaking vs Decisionmaking
Different processes:
Policy:
Typically oriented towards broader audiences
Longer time horizons
Decision
Cognitive and psychological factors
Smaller groups and shorter time horizons
Policy
- Typically oriented towards a broader audience. Policy is often designed and implemented with an eye towards achieving broad political goals and appealing to broad audiences.
- Domestic political supporters and party activists, for example.
- For this reason policy can often be vague, and how presidents choose to implement policy gets into the realm of decision.
- Also typically involves longer time horizons. This is something presidents choose for the course of an administration.
Decision
- Cognitive and psychological factors are often at work when it comes to decision-making.
- Policymakers often exaggerate or inflate an enemy’s potential.
- Analogies are also often invoked to help make decisions (policy too).
- Smaller groups: Makes decision-making somewhat easier, but individual personalities become more influential. Politics still matter, though.
- Example: William Bundy’s memo on getting out of Vietnam—only a small group of policymakers ever saw the document before squashing it. Daniel Ellsberg who leaked the Pentagon Papers saw a copy.
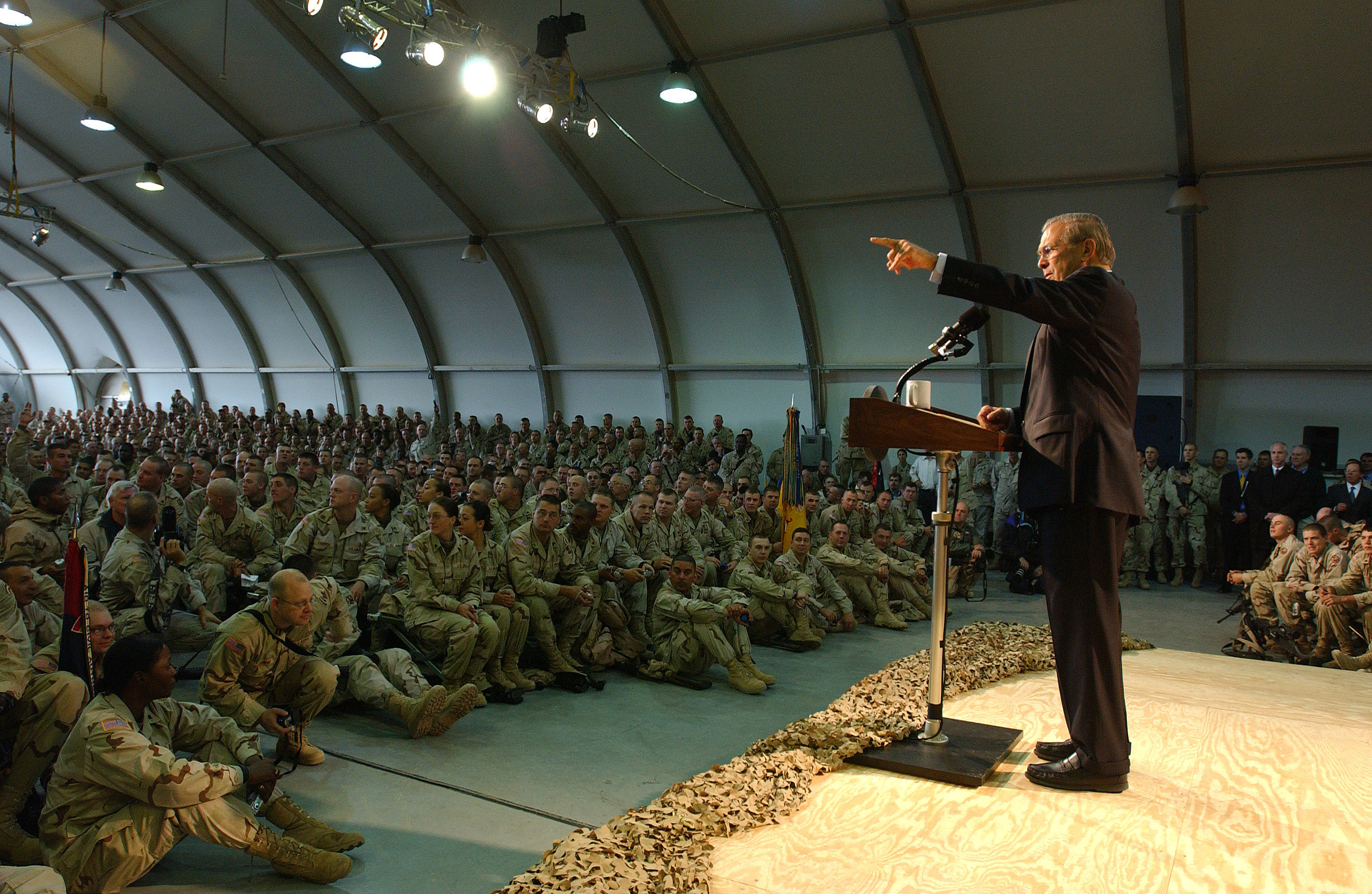

Influence of Policy on Decision
- Slide of Donald Rumsfeld speaking to US troops in Kuwait, 2004.
- Policy can impose constraints on what actions you can take.
Rumsfeld fielded a question from Army Spc. Thomas Wilson of the 278th Regimental Combat Team who complained that military vehicles are not properly armored:
"Now why do we soldiers have to dig through local landfills for pieces of scrap metal and compromised ballistic glass to up armor our vehicles, and why don't we have those resources readily available to us?"
Rumsfeld replied:
"As you know, you go to war with the army you have, not the army you might want or wish to have at a later time. Since the Iraq conflict began, the Army has been pressing ahead to produce the armor necessary at a rate that they believe -- it's a greatly expanded rate from what existed previously, but a rate that they believe is the rate that is all that can be accomplished at this moment.”
This smaller leaner military was a result of Bush administration priorities. Not necessarily bad, but they did tie the administration’s hands in some ways.
The Bush administration entered office campaigning on lower taxes and against nation-building and the over-use of the American military abroad. The administration also wanted to focus on developing a lighter, more agile military with less emphasis on traditional heavy infantry and mechanized units.
From the 2002 National Security Strategy, page 29. Speech originally delivered by President Bush to a joint session of Congress on September 20, 2001:
“A military structured to deter massive Cold War-era armies must be transformed to focus more on how an adversary might fight rather than where and when a war might occur…Before the war in Afghanistan, that area was low on the list of major planning contingencies…We must prepare for more such deployments by developing assets such as advanced remote sensing, long-range precision strike capabilities, and transformed maneuver and expeditionary forces.
Rumsfeld’s 2001 Foreign Affairs article: Discusses the 2001 quadrennial defense review and the decision to eliminate the old two-front war doctrine. Shift is now to the ability to deter multiple aggressors, and maintain a force capable of occupying one enemy.
smaller, lighter force can be useful, but we quickly discovered that this wasn’t enough in an attempt to occupy and rebuild two countries.

Trump and the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action
Trump campaigned on his opposition to the Iran nuclear deal, otherwise known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action
- Negotiated between United States, China, France, Germany, Russia, the UK, the European Union, and Iran.
- Adopted October 18, 2015 and implemented on January 16, 2016
- Intended to limit the development of nuclear technology by the Iranian government to peaceful purposes.
Placing so much emphasis on his opposition to the Iran nuclear deal effectively limited Trump’s ability to maintain the deal or to negotiate changes preferable to the United States. This was in spite of recommendations from Trump’s national security team to keep the deal.
Trump announces US is breaking the deal on May 8, 2018.
Secretary Pompeo has subsequently references Iran's post-US withdrawal non-compliance as a justification for abandoning the deal.
Policymaking Organization
Policymaking Organization
National Security Act of 1947:
Created the basic bureaucratic organizations, positions, and structures we now use
Intended to standardize national security policy- and decision-making
Promote cooperation
National Security Act of 1947:
- Created the basic bureaucratic framework to guide decision making and policymaking.
- Created to remedy issues related to cooperation and interservice rivalry in World War II
- Also intended to address FDR’s highly personalized leadership style and lack of clear organization.
- Creates:
- National Security Council
- National Military Establishment. Later Amended in 1949 to become the Department of Defense.
- Secretary of Defense
- Central Intelligence Agency
Policymaking Organization
Bureaucratic organizations:
Organizational mandates and roles inform positions and policy preferences
Develop expertise in particular areas
Carry out basic functions of government
Bureaucratic Organizations
- Organizational mandates and roles inform positions and policy preferences
- Develop expertise in particular areas
- Carry out basic functions of government
- As federal bureaucracy becomes larger, we often find that organization don’t communicate with one another. Designed to make sure everyone is on the same page.
Policymaking Organization
National Security Council:
Designed to promote inter-agency cooperation and coordination
President chairs all NSC meetings
Statutory members:
- President
- Vice President
- Secretary of State
- Secretary of Defense
- Secretary of Energy
- Secretary of the Treasury
- Director of the Office of Pandemic Preparedness and Response
- Such other officers of the United States Government as the President may designate
Organization of the NSC
- Chaired by President
Statutory Members include:
- President
- Vice President
- Secretary of State
- Secretary of Defense
- Secretary of Energy
- Secretary of the Treasury
- Director of the Office of Pandemic Preparedness and Response
- See here for US Code
Formerly included:
- Director of Mutual Security (defunct, initially oversaw the distribution of economic and military assistance)
- Chair of the National Security Resources Board (defunct, focused on long-term planning and mobilizing economic resources in case of war).
- Service Chiefs (Army, Navy, Air Force)
Statutory Advisers:
- Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is the principal military advisor to the president and to the NSC. May attend and participate in meetings of the NSC.
- Director of National Intelligence (DNI)
Others who can/do participate regularly:
- Basically the president can determine who else joins in on meetings, so NSC can look different from administration to administration
- Chief of Staff
- Counsel to the President
- Director of the National Economic Council
- National Security Adviser
- Secretary of the Treasury
- US representative to the United Nations
Principals Committee is the primary senior inter-agency forum for NSC issues and planning. “The Principals Committee (PC) shall continue to serve as the Cabinet-level senior interagency forum for considering policy issues that affect the national security interests of the United States.”
- Was in the news a lot during the early Trump administration when Steve Bannon, the president’ chief political strategist, has been given a place on the NSC, and on the Principal’s Committee. Also because CJCOS has been removed as mandatory regular participant of NSC/PC. See here for memorandum outlining membership at the beginning of the Trump Administration. This was rescinded in April by another memo.
- Deputies Committee is similar, but consists of agency deputies.
- Executive staff. NSC is broken down into a number of issue planning committees. Staff size has varied over time and current debates center around shrinking the size of the NSC.
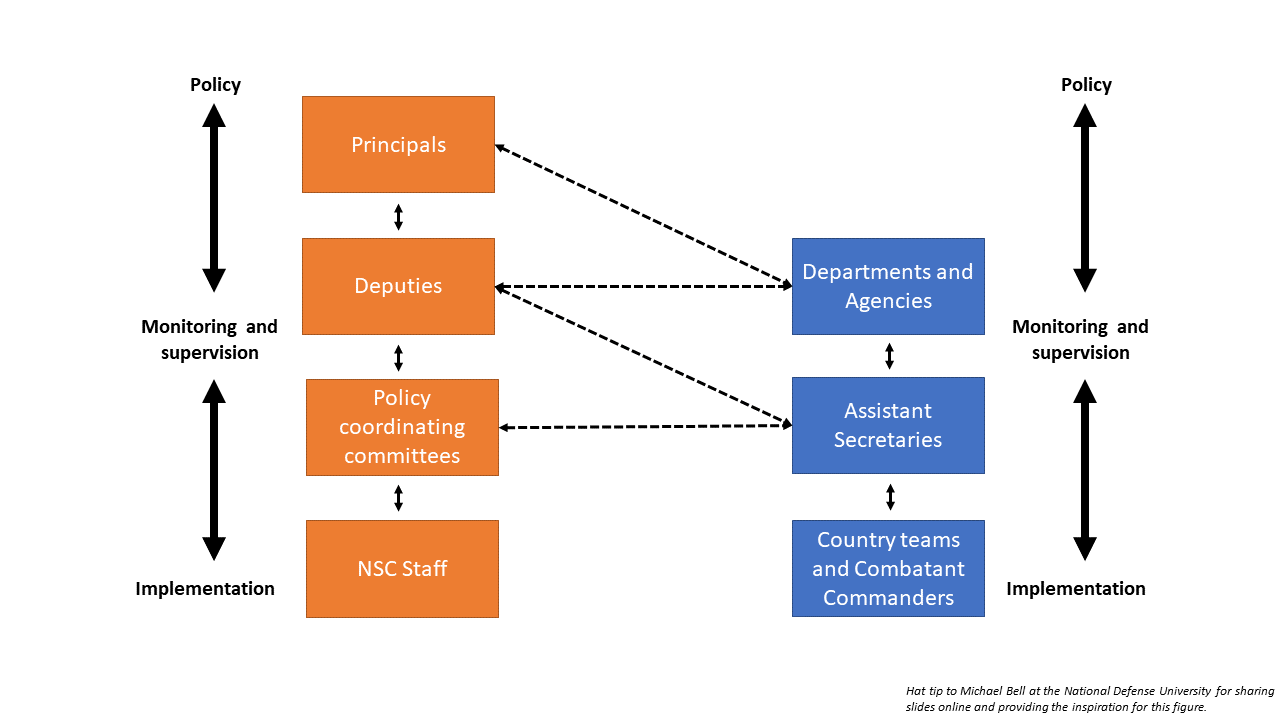
Diagram showing NSC
Top-level policymaking occurs with the principals committee
Deputies committee responsible for starting the implementation process and monitoring the activities of the variation coordinating committees
Policy coordinating committees typically occur at the Assistant Secretary level. Responsible for working to implement NSC guidance back in individual departments.
Also note that principals and deputies can act within their own agencies/departments, too.
There are also a lot of informal mechanisms by which individuals coordinate policy action. Presidents often have breakfast with different members of his team or heads of agencies to talk about key issues.
Also the NSC staff
- Some permanent staffers (~50)
- Other staffers are assigned to NSC from parent agencies (military service, DOD, State, etc.)
- NSC is limited to 200 staffers by statute.
Policymaking Organization
Political factors:
Policymaking intimately tied to politics
Campaign promises and constituencies affect policies and related decisions
Presidents continue to monitor constituent preferences
Policy is guided by politics
- Policy is informed by political preferences. Presidents may be constrained in some ways if certain policy options are not in line with ideological views or constituent preferences.
Policymaking Pitfalls
Policymaking Pitfalls
The ideal process:
Full information
Broad range of options are considered
What does the ideal look like?
- Information obtained from all available sources. Collect as much intelligence as possible. What information does an administration have or not have?
- Facts coordinated and distilled (Director of Central Intelligence and National Security Advisor). Were some sources of information suppressed?
- Broad range of options considered
- What options were considered? Diplomatic? Military?
- Costs and benefits specified for each option? Biased presentation of options by State, Defense departments?
Policymaking Pitfalls
Breakdowns in information search
Reliance on single information channels
Reliance on analogies
Motivated information search
Possible problems
-Breakdowns in information search (cover each on subsequent slides)
Reliance on a single information channel
- Policymakers rely too much on specific sources of information.
- Even if those sources are acting in good faith, they may not possess all the facts.
- Worst case, source is compromised.
- Can lead to skewed assessments, or bias policymaking in favor of some options over others.
Reliance on analogies
- Policymakers often like to rely on historical analogies to guide policy. This is reasonable, but can cause problems
- Not all cases are identical, even if they look similar
- Relying on Vietnam as a lesson in fighting an insurgency/guerilla war can lead to bad conclusions. Not every insurgency looks like Vietnam.
Motivated information search
- Policymakers know the policies/conclusiosn they want, and so they look for information that fits with that narrative.
- This is what happened with the Iraq War.

Iran and the Shah
- US embassy and CIA largely reliant on the Shah for intelligence. This presented them with a distorted view of domestic stability.
- Shah suppressed alternative sources.
- Accounts suggest that Colin Powell was frozen out of the Bush administration’s deliberations. This prevents him from giving advice.

Use of analogies: Chamberlain, Hitler, Munich, and Appeasement
- Western leaders believed that Hitler could be appeased. Negotiated annexation of Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia to Hitler’s Germany. Hitler goes on to ravage Europe.
- Dubious conclusion is that all diplomatic negotiations are dangerous.
- Ignores particular details about a case that may set it apart from other cases.
- Vietnam example: Multiple conflicts compared to Vietnam (e.g. Afghanistan). Vietnam itself compared to the loss of China

Munich parallel to Iran negotiations
- Large power disparities between Iran and the US.
- Not clear that Iran's goals are at all similar to Germany's. No clear territorial ambitions requiring regional conquest.
- Iran surrounded by wealthy and heavily armed nations hostile to it, many of whom all have established relationships with hardened militant organizations.
- Limited military strikes unlikely to be effective. Full military invasion not feasible, and effectiveness is dubious. Likely to result in numerous fatalities.
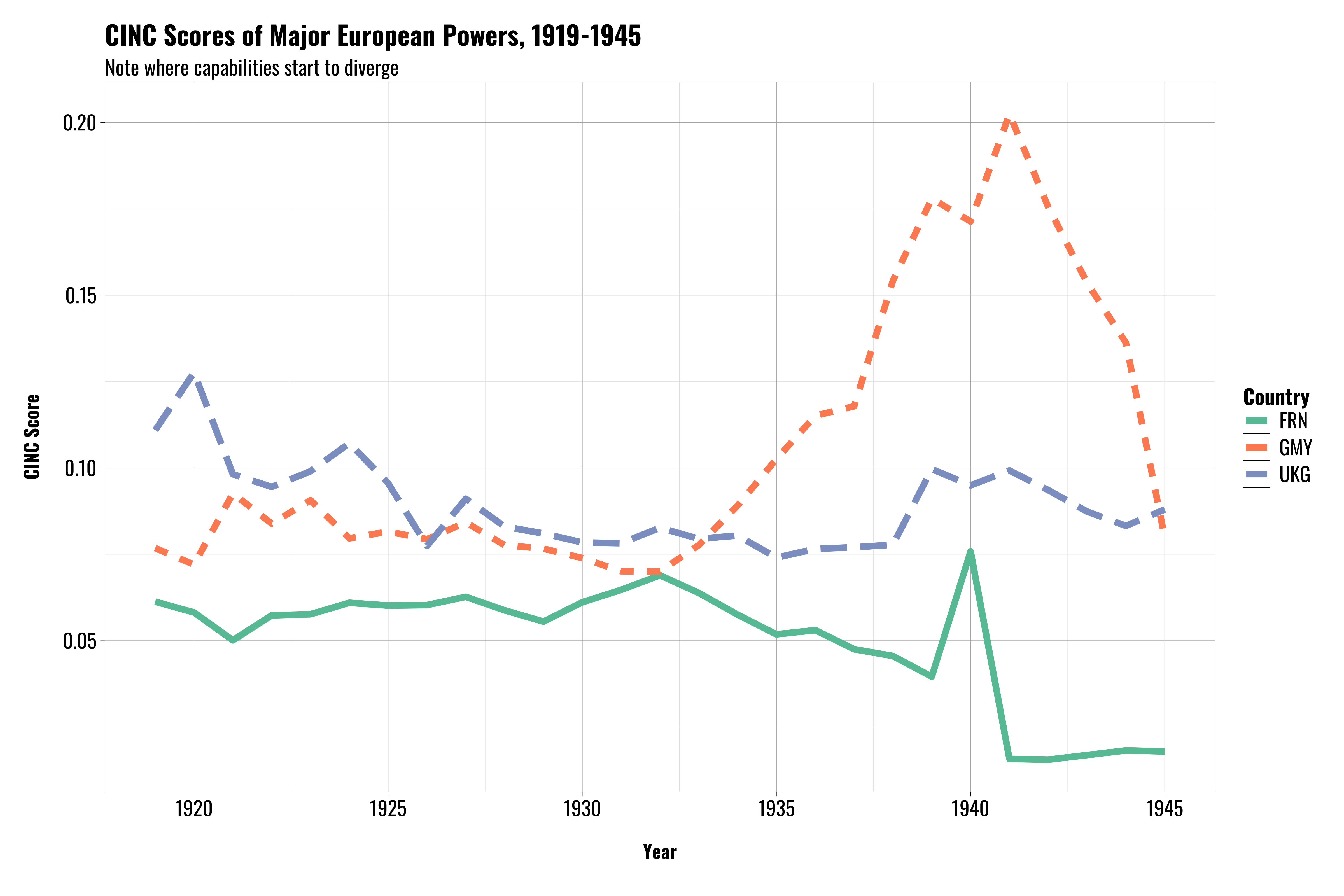
Capabilities in 1930s
- Note that capabilities are much closer here (trajectory can be hard to see at the time)
- Not all the allies were on the same page regarding Germany's status at the end of WWI, so some were inclined to be more permissive as Germany rebuilt.
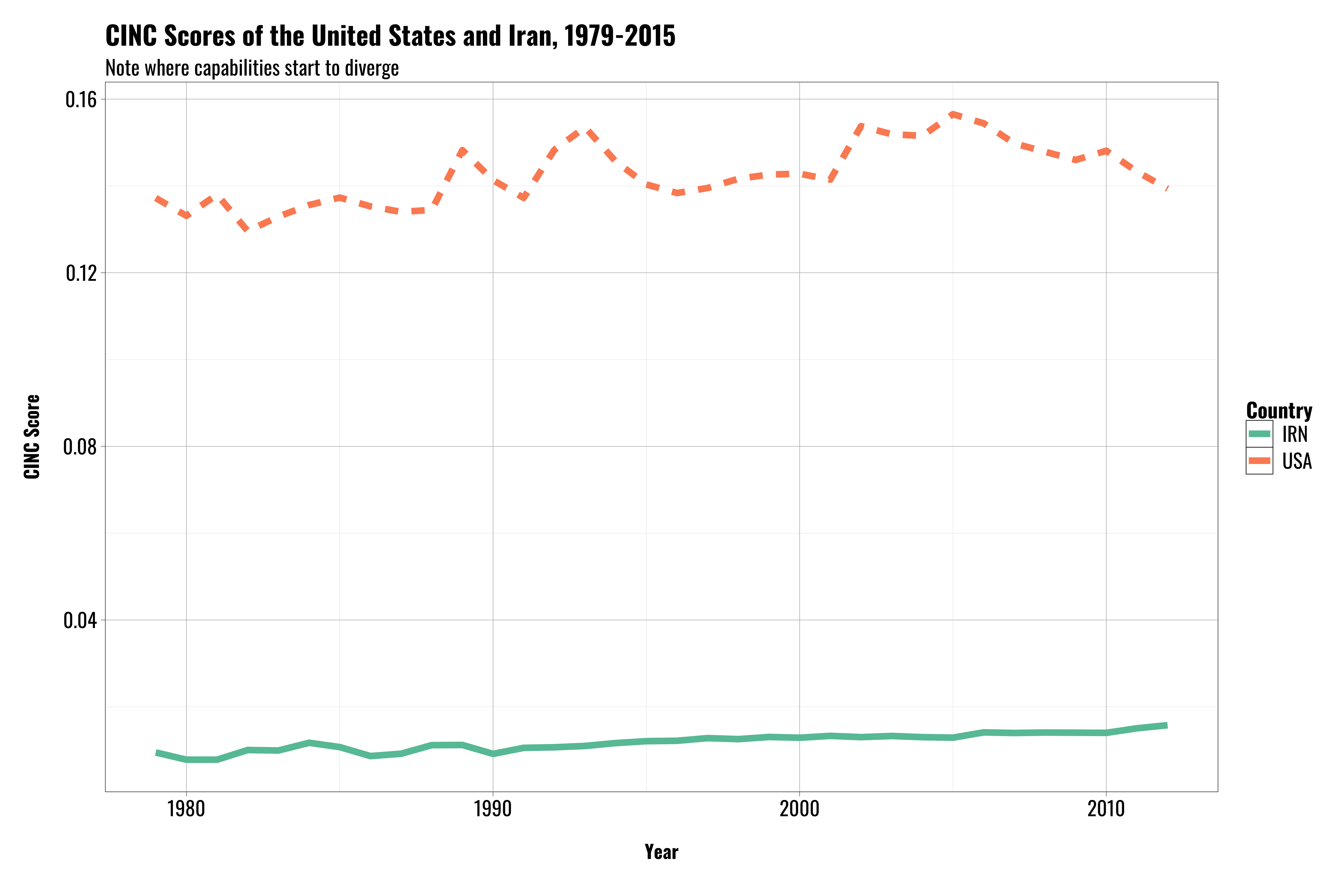
Capabilities today
- The environment looks a lot different today
- US is clearly more powerful than Iran
- Iran is in a very different regional environment, too.


Bureaucratic rivalries and skewed assessments
- Policymaking can be thrown off by internal inconsistencies or bureaucratic rivalries.
- Critics suggest Mike Pompeo provided President Trump with overly optimistic views of North Korea’s willingness to give up its nuclear weapons, thus prompting Trump to push for negotiations and to hold unrealistic views of what was feasible.
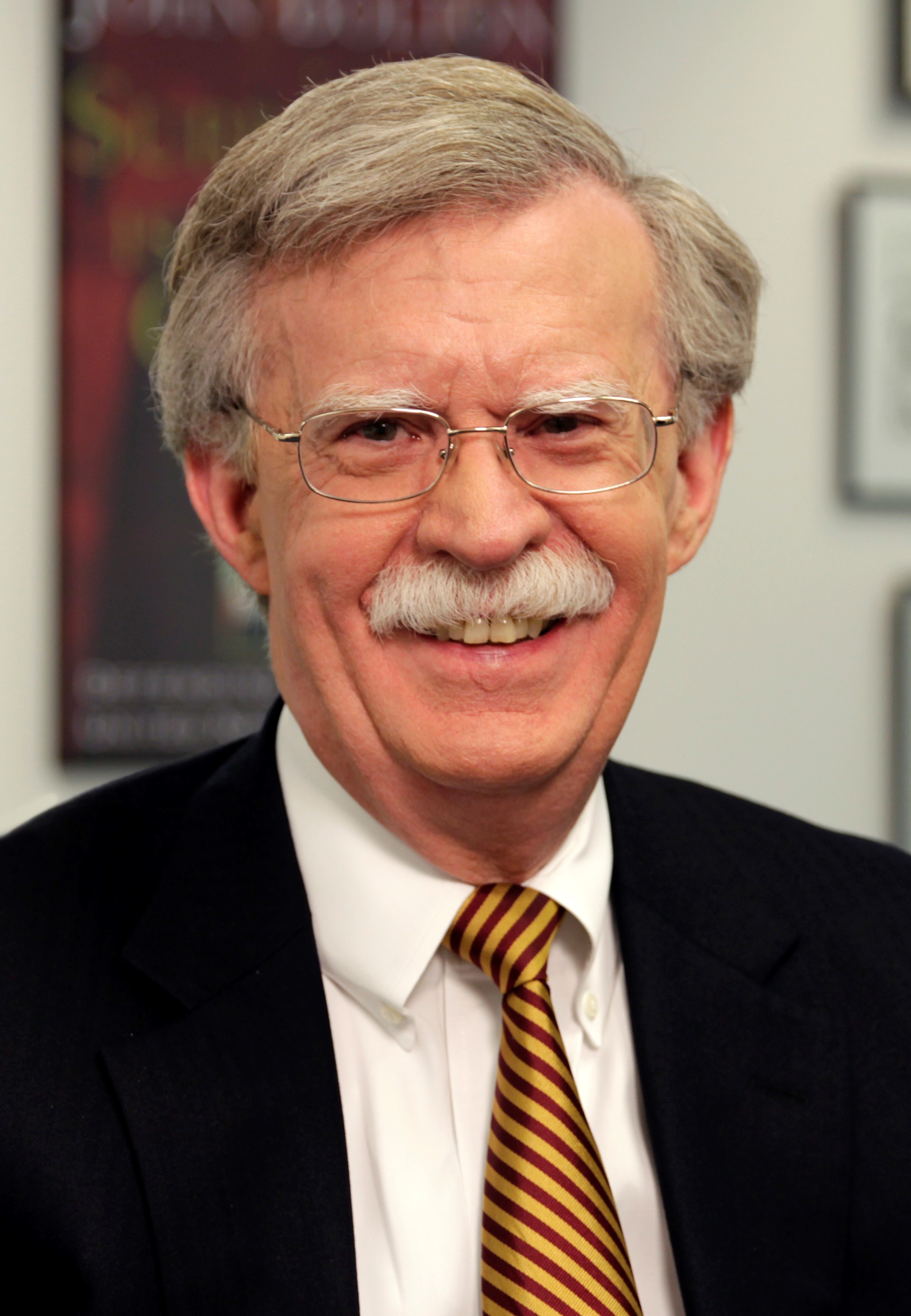
- John Bolton has long opposed negotiating with adversaries of the United States. In the lead up to the June 12, 2018 Singapore meeting between Trump and Kim Jong Un, Bolton couched negotiations in the context of the “Libya Model”, referring to Muammar Gadaffi’s decision to give up his WMD program in 2005. He was subsequently killed by rebels in 2011 after the US and allied states provided air support to rebels.
- Suspicion is that Bolton purposely tried to sabotage the negotiations so as to promote a more hard-line agenda.
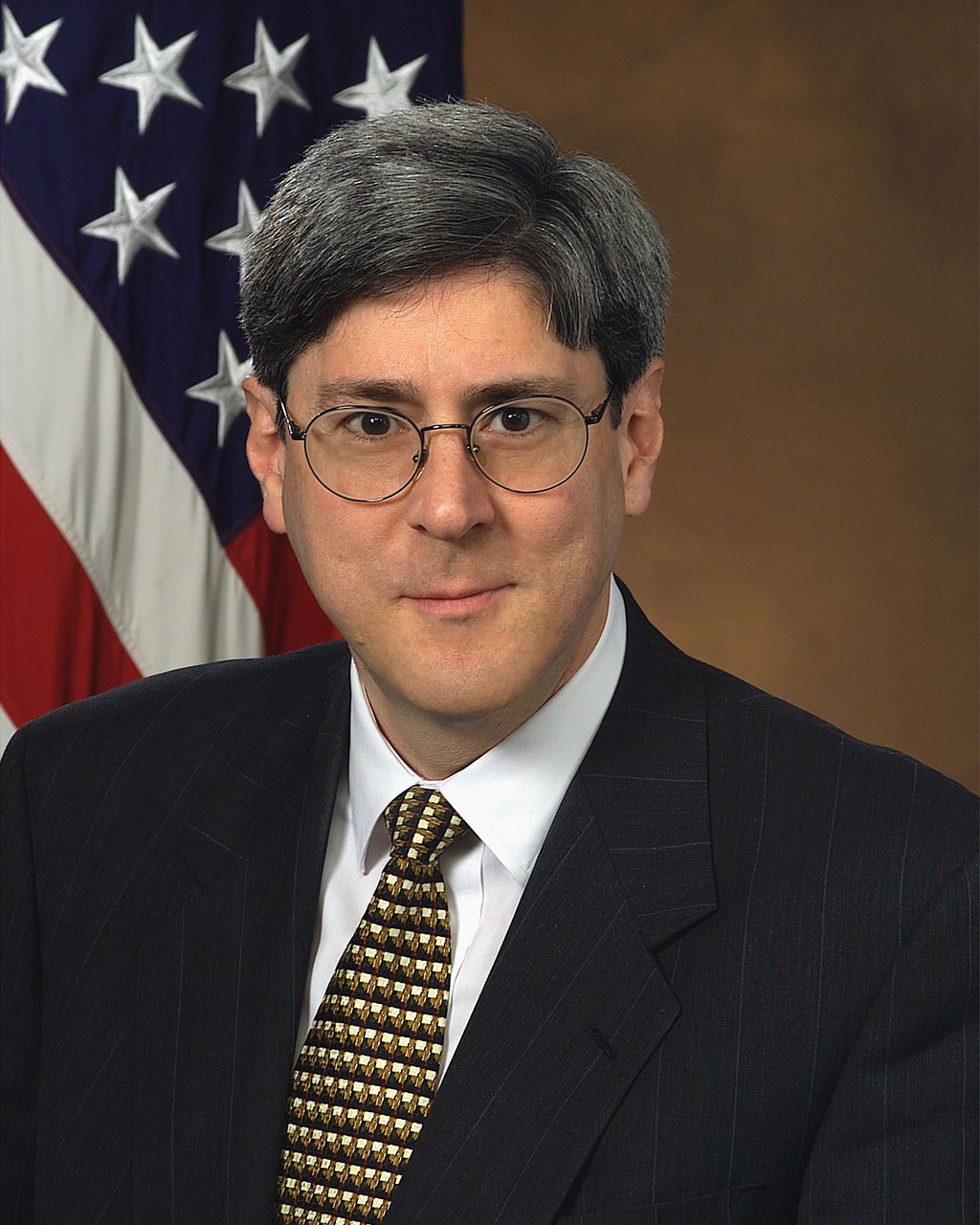

Motivated information search: Example Doug Feith in Bush administration.
- General tendency to find information that conforms to the way you see the world. Rather, preferred policy influences what you see.
- Doves will see opportunities for peace where there is none (Munich)
- Hawks will see enemies as stronger than they are because it justifies more aggressive policies (Iran)
- These dynamics are made worse when advocates of particular policies also provide information to top policymakers
- Doug Feith and the Office of Special Plans. Office was set up to provide intelligence to the Bush administration that was in line with the desired policies. Specifically, information that supported the US invasion of Iraq. Was also in charge of postwar planning, which as we all know didn’t turn out so well. Also in charge of the Counterterrorism Evaluation Unit.
- This is the organization that produced intelligence “linking” al Qaeda to Iraq and Saddam Hussein. General Tommy Franks is quoted in Bob Woodward's Plan of Attack as saying that Douglas Feith is "the fucking stupidest guy on the face of the earth.”

Second example of motivated information searching: Intelligence evaluations of ISIS and Taliban
- Intelligence assessments of ISIS and the Taliban come under attack as being manipulated to overstate successes and downplay failures.
Policymaking Pitfalls
Not considering all the options
Sometimes politicians might not consider every possible option
Some options might be eliminated immediately because they're not politically desirable
Bureaucratic officials or advisers may manipulate the range of options presented